A hysterectomy is one of the most common surgical procedures among women. According to Ms. Summer V. Harvey, M.P.H., Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics, National Cancer Institute, 9609 Medical Center Dr., Rockville, MD approximately 600,000 hysterectomy procedures are performed annually in the United States (U.S.). Although in most cases a hysterectomy is performed for medical reasons and can be life-saving, it inevitably becomes a significant challenge – both physically and emotionally.
For many women, a hysterectomy not only means the loss of an organ but also the inability to carry a child. This realization can lead to feelings of loss, anxiety, and even depression. However, modern advancements in reproductive medicine offer hope: motherhood after a hysterectomy is possible thanks to assisted reproductive technologies (ART) and surrogacy.
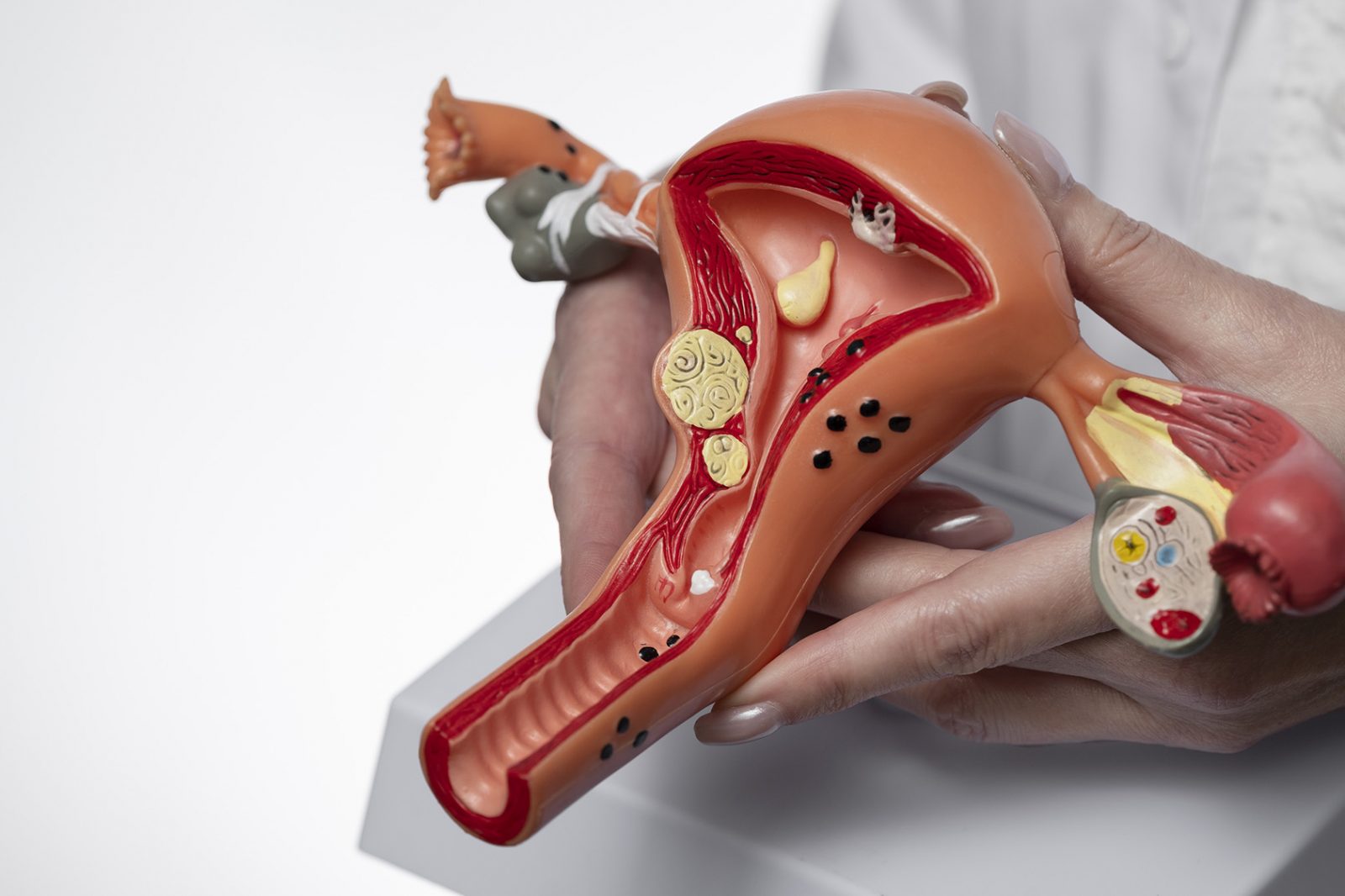
The Impact of Hysterectomy on Reproductive Functions
A hysterectomy completely eliminates the possibility of carrying a child, as the uterus is the key organ responsible for embryo implantation and development. However, the degree of impact on the reproductive system depends on the type of procedure:
- Total Hysterectomy (Complete Uterus Removal). This involves the removal of both the uterus and the cervix. Reproductive function is entirely lost, but if the ovaries are preserved, a woman can still use her eggs for in vitro fertilization (IVF), with the resulting embryo carried by a surrogate mother.
- Subtotal (Supracervical) Hysterectomy. In this procedure, only the uterus is removed, while the cervix remains intact. The impact on hormonal balance is minimal, but the ability to become pregnant is still lost.
- Hysterectomy with Ovary Removal (Hysterosalpingo-oophorectomy). In this case, a woman not only loses the ability to have children but also enters surgical menopause, as ovary removal causes a sharp decline in estrogen and progesterone levels.
Hormonal Changes After Hysterectomy
If the ovaries remain, they continue to produce hormones, although their function may gradually decline over time. If the ovaries are removed, artificial menopause develops, accompanied by typical symptoms such as hot flashes, vaginal dryness, weight changes, and deteriorating skin and bone health.
Despite losing the ability to carry a pregnancy naturally, women who have undergone a hysterectomy still have the chance to become mothers. Modern reproductive technologies, including IVF with their own or donor eggs and surrogacy, enable women to experience the joy of motherhood even after such a major surgery.
Motherhood Alternatives After Uterus Removal
For women who have undergone a hysterectomy, the inability to carry a child themselves does not mean that motherhood is an unattainable dream. Modern reproductive medicine offers an option that allows a woman to become a biological mother – surrogacy.
What Is Surrogacy?
Surrogacy is a method of assisted reproductive technology (ART) in which another woman (a surrogate mother) carries and delivers a child for the genetic parents. The embryo is created through in vitro fertilization (IVF) and then transferred to the surrogate mother’s uterus.
If a woman who has undergone a hysterectomy previously froze her eggs, this is the ideal scenario: the child will be fully genetically related to her and her partner. If no eggs are preserved, donor oocytes can be used.
How Does the Surrogacy Process Work?
The process involves several stages:
- Finding and Preparing a Surrogate Mother
- The surrogate mother must meet medical requirements: she should be healthy, have at least one child of her own, and have no contraindications for carrying a pregnancy.
- Candidates typically undergo medical and psychological evaluations.
- Creating an Embryo via IVF
- If frozen eggs are available, they are fertilized with the partner’s sperm.
- If no eggs are available, donor eggs can be used.
- The resulting embryos are cultivated in a laboratory before being transferred to the surrogate mother’s uterus.
- Pregnancy Management
- Throughout the pregnancy, the surrogate mother is monitored by medical professionals.
- Intended parents can actively participate in the process, overseeing medical aspects and maintaining communication with the surrogate mother.
- Childbirth and Legal Procedures
- After delivery, the baby is handed over to the biological parents.
- Legal matters arise at this stage, as surrogacy laws vary by country.
Legal Challenges of Surrogacy
Surrogacy is not universally accepted and may be prohibited or strictly regulated in some countries, often forcing couples to seek options abroad.
- In certain countries, biological parents must undergo complex adoption procedures to gain legal recognition as the child’s parents since the law recognizes the birth mother as the legal mother.
- Some nations permit surrogacy only for their citizens, restricting access for foreign couples.
- Other countries have well-established legal frameworks for surrogacy that protect the rights of all parties involved.
Before starting the process, it’s crucial to choose a country where commercial surrogacy is legal and ensures that you, as biological parents, receive full legal rights.
Where Can You Undergo a Surrogacy Procedure?
Ukraine is one of the few countries where commercial surrogacy is legally permitted and available to foreign citizens. This makes it an attractive destination for couples who are unable to carry a child on their own.
Advantages of Ukraine for Surrogacy
- Clear Legislation
Ukrainian family law recognizes biological parents immediately after the child’s birth. The birth certificate lists only the genetic parents, not the surrogate mother.
- High Standard of Reproductive Medicine
Ukrainian reproductive clinics are equipped to meet global standards, and doctors have extensive experience in assisted reproductive technology (ART). The success rate of pregnancies following IVF in Ukraine is among the highest in the world.
- Program Availability for Foreigners
Unlike many other countries, there allows foreign couples to legally participate in surrogacy programs in Ukraine. The only restriction is that participation is permitted exclusively for heterosexual couples who are legally married.
- Financial Affordability
The cost of surrogacy in Ukraine is lower than in countries where this procedure is legal (such as the United States or Canada), while the quality of medical services remains high.
Ukrainian laws clearly protect the rights of biological parents:
- After the child is born, the surrogate mother has no legal rights to the child.
- The birth certificate immediately lists the biological parents.
- The document processing procedure is as simplified as possible.
Ukraine has become one of the leading global centers for surrogacy due to its combination of affordability, highly qualified specialists, and legal protection for future parents.
A past hysterectomy is not a verdict for a woman dreaming of having a child. Modern reproductive technologies offer the chance to experience motherhood even in the most challenging situations.
The key is not to lose hope. Advances in modern medicine open the door to long-awaited motherhood, even when it seems that door has already closed.


